|
This software is a distributed architecture general-purpose information exchange software designed and developed by Jindeke Information Development Co., Ltd. to achieve code reuse and improve project development speed and reliability, based on the summary of project development experience. By introducing an information exchange platform, business logic can be modularized, parallel module development, version control, and coordinated management can be carried out during software project development. Implementing a unified module interface, coordinating resource allocation between modules, scheduling operations, and ensuring loose coupling between modules can achieve code level reuse and management of business and basic functional modules. Adopting a network distributed architecture design, it can achieve network deployment, module level load balancing, and redundancy functions for business projects. The software uses a simple graphical operation method for module configuration and operation monitoring, with a user-friendly interface. 1. Design conceptBased on code level software reuse and universal information exchange platform software. It is possible to modularize business logic and ensure loose coupling between modules. Coordinate resource allocation among modules, schedule operations, and establish a unified and user-friendly information exchange interface between modules. A project management tool for module parallel development, debugging, and version management. Use a simple graphical operation method for module configuration and operation monitoring, with a user-friendly human-machine interface. 2. System architecture diagram
3. Working principle1) The basic function development team uses module templates to write some technically strong basic modules in the project that are not closely related to business logic. 2) Each group uses module templates in parallel to write code for each business module and compiles it into module DLLs. The module template contains a universal information exchange interface implementation for the module, and programmers only need to focus on the implementation of business logic.
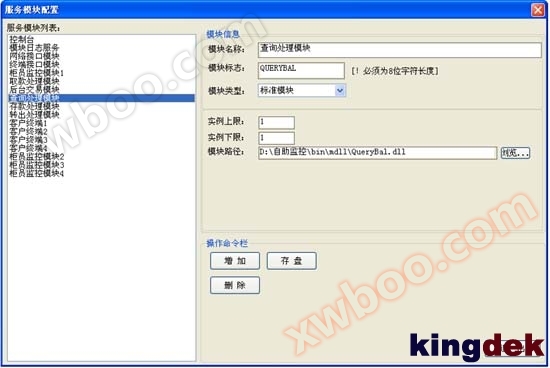
3) After the module is developed, the integration programmer runs the configuration tool software and adds each compiled module or reusable module with the same function from previous projects to the system in the configuration interface of the information exchange platform, and sets the corresponding parameters.
4) Run the KSwitch information exchange platform server program, which loads each module into memory according to the configuration file, assigns information ports to each module, establishes an information exchange and transmission mechanism, and monitors the running status of each module.
5) Each module runs and exchanges information with other modules according to a unified interface. 6) The distributed network module can deploy and run each module in a distributed manner according to its configuration. 7) The system performs load balancing based on operational monitoring and scheduling rules. 8) When the system is deployed in a distributed redundancy mode, the system detects the status of network and device resources, switches module deployment in the event of a failure, and completes the redundancy function. 9) Display the running status of each module on the monitoring client of the information exchange platform, and also view logs on this tool. This tool can run on any machine that is network connected to the server, and present the system's operating status through a network connection. () |