
1、 Main performance parameters of 6YL-125 spiral oil press:
Squeezing shaft speed: 35-39 revolutions per minute
Gearbox transmission ratio: 15/381552=1:8.78
Power supply: 15KW
Triangle Belt: Type B
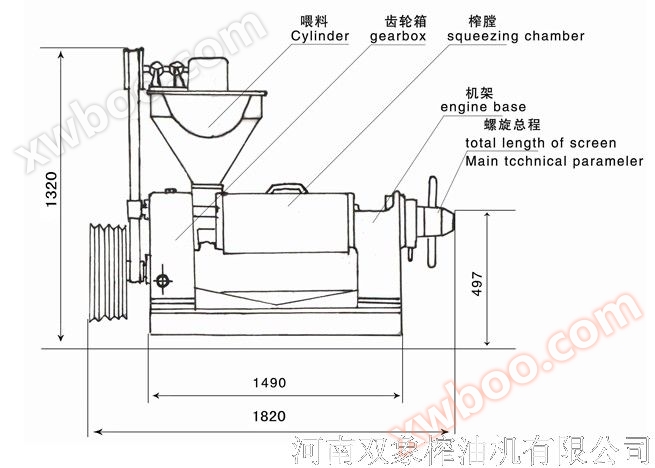
Dimensions: Length x Width x Height 1820x570x1320 (mm)
Unit weight: 580kg
Production capacity is shown in Table (1)
|
Oil name raw material |
each24Hourly processing capacity(ton) feeding per hour(t) |
Oil production per 100 kilograms(kg) Oil output per 100kg raw material |
Dry cake residual oil rate(%) residue(%) |
|
rapeseed rape seeds |
5-7 |
30-38 |
7.5-8 |
|
peanut Ground nuts |
5-7 |
35-45 |
7 |
|
soybean Bin |
5-6 |
10-16 |
6.5-7 |
|
sesame sesame |
6-7 |
44-47 |
6.5-7.5 |
|
cottonseed Cotton seeds |
4-5 |
10-14 |
5.5-6.5 |
Note: The above parameters refer to the complete selection, separation, and rolling auxiliary equipment, reasonable process, and normal operation that can achieve the indicators.
2、 Working principle and structure of 6YL-125 spiral oil press:
1. Working principle:
When the oil press is running, the processed embryo is carried into a hopper, and the oil enters the press chamber from the hopper. The spiral with a squeezing screw is pushed inward for squeezing.
Due to the fact that the embryo is in operation within the oil press chamber, significant frictional resistance is generated between the embryo, the screw, and the chamber under high-pressure conditions. This can cause friction between the raw material and the raw material, resulting in relative motion. On the other hand, the diameter of the root circle of the squeezing screw gradually increases. When the squeezing screw rotates, the thread allows the embryo to both move forward and flip outward. At the same time, the material layer near the surface of the squeezing screw thread rotates with the squeezing shaft, so that each embryo particle in the squeezing chamber does not move at the same speed and direction. And there is also relative motion between particles. The heat generated by friction satisfies the necessary heat for the oil extraction process, which helps to promote the thermal denaturation of proteins in the embryo, destroy colloids, increase plasticity, and reduce the viscosity of the oil, making it easy to separate and extract oil, thus improving the oil extraction rate of the oil press.
2. Structure: The machine consists of five main parts: feeding hopper, gearbox, pressing chamber, pressing screw, and frame, as shown in the figure
(1)
3、 Installation of the machine:
The oil press must be installed on a solid foundation with anchor bolts to keep the machine level. The motor is installed on the back of the feeding hopper.
4、 Lubrication of the machine:
1. Oil presses mainly use two forms of lubrication: oil and butter. The refueling cycle is shown in Table 2
|
serial number NO |
Lubrication parts lubrication |
Types of oils and fats lubricate |
Refueling cycle Tname span |
Oil change interval Lubricatereplacement period |
1 |
Adjusting bolt Adjustingbolt |
20Mechanical oil Mechanical oil NO.20 |
per class2time 1-2time/day |
|
2 |
bevel gear Blike a pair |
20Mechanical oil Mechanical oil NO.20 |
per class2time 1-2time/day |
|
3 |
bearing sleeve Bearing bush |
20Mechanical oil Mechanical oil NO.20 |
per class2time 1-2time/day |
|
4 |
gearbox Gearbox |
20Mechanical oil Mechanical oil NO.20 |
First refueling12kg |
six months |
5 |
Each rolling bearing bearing |
lubricating oil Grease |
once a year |
Five Machine operation:
(1) Key points before starting up:
Before starting up, fill the gearbox with 12 kilograms of engine oil
After installing the machine, add lubricating oil according to regulations, check whether all components are fastened, and whether the operating handle and plug plate are flexible
3. Use your hands to move the large pulley and check for any looseness or jamming of the machine. If there are any abnormalities, promptly eliminate them
4. Adjust the tightness of the belt, start the motor, and check if the direction of the pulley is consistent with the marked direction
After the preparation work for the inspection is completed, loosen the locking nut and screw the press screw to the dead center, then retract 3-4 turns, and move forward half a turn to ensure the gap between the press screw and the cake outlet
6、 General faults and troubleshooting methods of spiral oil press
serial number |
fault |
root cause |
exclusion method |
|
1 |
Suddenly stopped, the screw press shaft got stuck. |
1. The new machine was used for initial pressing, but a large amount of material was fed into the press without running in. 2. The thickness of the cake is too thin, which increases the pressure in the squeezing chamber. |
1Follow the instructions and pay attention to the sound and current intensity of the machine frequently. |
|
2 |
Over bottom oil discharge |
1. The moisture content of the oil is not suitable. 2. The temperature inside the squeezing chamber is low. 3. The gap between the strip and circular rows does not meet the requirements. 4. Parts wear and tear. |
1. Operate according to the instructions. 2. Loosen or tighten the compression nut to allow a small amount of slag to flow smoothly. |
|
3 |
Storage of oil in hopper (return oil) |
1The circular bars are arranged too tightly. 2The oil content in the oil is too high, and the cake is too thin. |
1Loosen and tighten the nut to ensure smooth oil flow. 2Adjust the thickness of the cake and add it to the squeezing chamber to flush out the oil. |
|
4 |
Cake replaces oil stains |
1. Excessive moisture content in oil crops. 2. The clearance between circular rows is too small. 3. Parts wear and tear. |
1.Operate according to the instructions. 2.Loosen and tighten the nut to increase the clearance between the circular rows. 3.Replace with new parts. |
|
5 |
Oil is dark brown and silky |
1. The temperature inside the squeezing chamber is low. 2. Excessive impurities in the oil. 3. Oil is too dry or moldy. |
1. Operate according to the instructions 2. Filter oil materials. |
|
6 |
low yields |
1. Squeezing untreated cottonseeds, the fibers are long and easy to build bridges and entangle shafts. 2. Squeezing the chamber, squeezing the snail is not smooth. 3. Oil contains too much moisture. 4. The gap between the cake outlets is too small. 5. Brown snail wear. |
1. Cottonseed shedding or screening. 2. After replacing the new parts, a period of break in should be carried out to make the screw press smooth. 3. Operate according to the instructions. 4. Replace with new parts. |
7 |
No feeding |
1. Oil containing oils return oil. 2. Oil crops are too wet (especially cottonseeds) |
1. Operate according to the instructions. 2. Cottonseed seeds need to be dehulled. |
|
8 |
Serious slagging |
1. The gap between the rows is too large. 2. Excessive pressure in the squeezing chamber. 3. Parts wear and tear. 4. The oil is too dry. |
1. Operate according to the instructions. 2. Replace with new parts. |

